Blog
How to Configure IP CCTV Camera – Complete Step-by-Step Setup Guide (2025)
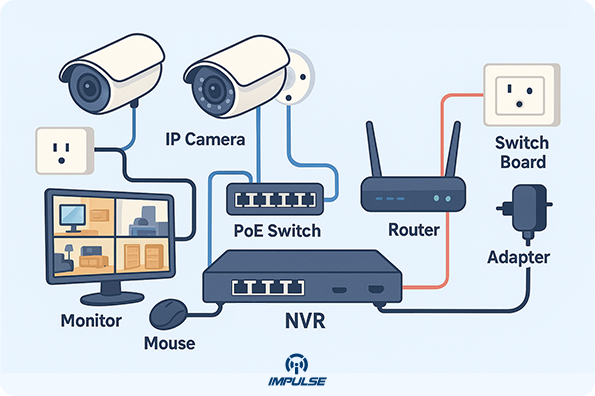
📸 Introduction – The Power of Smart Surveillance
In a digital-first world, IP CCTV cameras have transformed how homes and businesses monitor their surroundings. Unlike analog systems, IP cameras use your internet or local network to capture and transmit high-definition video. They offer crystal-clear footage, remote viewing, smart alerts, and easy scalability, making them the preferred choice for modern security setups.
But to unlock the full potential of an IP camera, you must configure it correctly. Whether you’re setting up one camera for home use or a full network of cameras for business surveillance, this detailed guide will walk you through everything you need to know about configuring IP CCTV cameras step by step.
🧩 1. Understanding What an IP CCTV Camera Is
An IP CCTV Camera, also known as an Internet Protocol Camera, is a modern surveillance device that uses a network connection (LAN or Wi-Fi) to transmit live video and audio signals. Unlike traditional analog CCTV cameras that rely on coaxial cables connected directly to a DVR, IP cameras send data digitally over your network — allowing high-quality video transmission, easy scalability, and remote access from anywhere in the world.
🧠 Key Concept:
Each IP camera is assigned a unique IP address on your network, just like a computer or smartphone. This address enables you to:
- Access the camera directly through a web browser or mobile app
- Integrate it with an NVR (Network Video Recorder) for centralized recording
- View and manage it remotely using the internet
🎯 Why IP Cameras Are Better Than Analog:
- Superior Image Quality: IP cameras support HD, Full HD, and even 4K resolution, offering crystal-clear footage.
- Two-Way Communication: Many models come with built-in microphones and speakers for real-time interaction.
- Remote Accessibility: Watch your live camera feed from any smartphone, tablet, or computer — anytime, anywhere.
- Scalability: You can easily add more cameras to the same network without complicated cabling.
- Smart Features: Advanced analytics such as motion detection, intrusion alerts, and facial recognition are supported.
- Flexible Storage Options: Record to an NVR, SD card, NAS, or even the cloud.
🏗️ How It Works – The Technical Flow:
- Video Capture: The camera’s image sensor captures real-time footage.
- Encoding: The video is compressed using codecs like H.264 or H.265 to reduce file size.
- Transmission: The encoded stream is sent over the network via Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
- Viewing & Storage: You can access it through software, a web interface, mobile app, or NVR for recording.
🧩 Example:
Let’s say you install an IP camera outside your shop. Once connected to your router, the camera receives an IP address like 192.168.1.120. You can then type this address into your browser or mobile app to watch live footage, adjust settings, or playback recordings — all in real time.

⚙️ 2. Pre-Setup Requirements
Before you begin configuring your IP CCTV camera, it’s crucial to prepare the right tools, equipment, and network setup. A proper pre-installation checklist ensures your configuration runs smoothly without errors, connectivity drops, or IP conflicts. Think of this step as laying the foundation for a secure and efficient surveillance system.
🧰 A. Hardware Requirements
Here’s what you’ll need to start your setup process:
- IP CCTV Camera (Wired or Wireless)
Choose a reliable brand such as Hikvision, CP Plus, Dahua, Realme, or Godrej. Make sure your camera supports ONVIF protocol (for universal compatibility with NVRs and software). - Power Supply or PoE Switch
- If your camera is non-PoE, use a 12V DC adapter.
- If it’s PoE-enabled (Power over Ethernet), a single Ethernet cable can transmit both power and data, simplifying installation.
- Network Router or Switch
A stable network connection is essential. Your router will assign IP addresses and link the camera, NVR, and computer together. - Ethernet (LAN) Cable – Cat5e or Cat6
Use high-quality Ethernet cables for stable data transmission. Cat6 is preferred for long runs or multiple camera connections. - Computer or Laptop
You’ll need a computer to access the camera’s interface, assign IP addresses, and perform initial configuration. - NVR (Network Video Recorder) – Optional
An NVR helps manage multiple cameras and stores video footage. Most modern NVRs automatically detect cameras on the same network. - Internet Connection (for Remote Access)
While local viewing doesn’t require the internet, remote monitoring via mobile apps does. Ensure your router is connected to an active internet line.
💻 B. Software Requirements
You’ll also need certain software tools to detect and configure your IP camera properly:
- IP Search or Device Management Tool
Every camera brand provides a free tool for detecting devices on your network:- Hikvision: SADP Tool
- Dahua: ConfigTool
- CP Plus: Device Manager
- Generic: ONVIF Device Manager
- Web Browser (with Plugin Support)
Many IP cameras have built-in web interfaces accessible through browsers like Internet Explorer, Edge, or Chrome (with extensions). Some older models require ActiveX or plug-ins for live view. - Mobile App (for Remote Access)
Download the official mobile app based on your camera brand:- Hik-Connect (for Hikvision)
- iDMSS/gDMSS (for Dahua)
- CP Plus ezykam+
- EZVIZ / Realme Link / Imou Life
- Firmware or Configuration File (Optional)
If your camera is new or not detected properly, you may need the latest firmware, available on the manufacturer’s website.
🔋 C. Environmental & Placement Preparation
Before installing your camera physically, plan your camera positioning and environment:
- Mounting Height: Install the camera 8–10 feet above ground level for optimal coverage.
- Field of View: Avoid direct sunlight or bright light sources.
- Network Range: Ensure Wi-Fi cameras are within 15–20 meters of your router for stable connectivity.
- Weather Protection: For outdoor cameras, use waterproof housing and proper sealing.
- Power Backup: Connect the camera or NVR to a UPS or inverter to avoid shutdowns during power cuts.
📋 Quick Pre-Setup Checklist
| Requirement | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply / PoE | Camera powered on properly | ✅ |
| Ethernet / Wi-Fi Connection | Stable and tested | ✅ |
| Router & Internet | IP range configured | ✅ |
| Computer Access | Administrator rights available | ✅ |
| Software Tools | Installed and ready | ✅ |
| Installation Area | Safe, secure, and reachable | ✅ |
Properly preparing your equipment and network ensures your IP camera configuration is quick, stable, and error-free. Once you’ve double-checked all these requirements, you’re ready to move on to the most crucial part — connecting the camera to your network.
🖥️ 3. Step 1 – Connecting the Camera to the Network
Now that you have all the necessary hardware and software ready, the next step in setting up your IP CCTV camera is establishing a stable network connection. This step ensures that your camera can communicate with your NVR, computer, and mobile app.
Depending on your camera type, you can connect it in two ways: through a wired Ethernet connection or a wireless Wi-Fi setup. Let’s go through both methods carefully.
🔌 A. Connecting a Wired IP CCTV Camera
A wired connection is always recommended for businesses, offices, and security-critical locations because it provides a more stable and interference-free signal.
🧭 Step-by-Step Setup (Wired):
- Connect the Camera to the Router or PoE Switch
- Take a Cat5e or Cat6 LAN cable.
- Plug one end into your IP camera’s LAN port and the other into your router or PoE switch.
- If your camera supports PoE (Power over Ethernet), the same cable will deliver both data and power — so no separate adapter is needed.
- Power On the Camera
- If it’s non-PoE, connect the 12V DC power adapter to your camera and plug it into a power source.
- Check the LED indicators (usually red, green, or blue lights).
- Flashing Light: Camera is initializing or connecting.
- Steady Light: Camera is powered and ready.
- Confirm Network Activity
- Look at the Ethernet port’s small LED lights on the camera or router.
- A blinking yellow or green light indicates data transmission — meaning your camera is successfully connected to the network.
- Verify Connection Using IP Search Tool
- Open the manufacturer’s IP Search Tool (SADP, ConfigTool, etc.) on your computer.
- The software will automatically scan and display connected devices.
- You’ll now see your camera listed with its default IP address (for example,
192.168.1.108).
- Note Down the IP Address
- You’ll use this IP address in the next step to log into your camera’s web interface.
- If multiple devices are detected, identify yours by checking the MAC address or device name.
📡 B. Connecting a Wireless IP CCTV Camera
Wireless IP cameras are ideal for home use or locations where running cables isn’t practical. They connect to your Wi-Fi network using the router’s SSID (network name) and password.
📱 Step-by-Step Setup (Wireless):
- Power On the Camera
- Plug in the DC power adapter and wait for the camera to boot up.
- Some cameras announce “Ready for Wi-Fi configuration” via voice prompts.
- Install the Mobile App or PC Software
- Download the official app from your camera’s brand (e.g., Hik-Connect, CP Plus ezykam+, Imou Life, Realme Link).
- Open the app and select “Add Device” or “Add Camera.”
- Scan the QR Code on the Camera
- Most cameras have a QR sticker with the serial number or UID.
- Scan this QR code using the mobile app.
- Connect to Wi-Fi
- Choose your home or office Wi-Fi network.
- Enter your Wi-Fi password and confirm.
- The camera will attempt to connect to the router. This process may take 30–60 seconds.
- Wait for Confirmation
- Once connected, the camera will announce, “Wi-Fi connected successfully.”
- Your app will now display the live video feed.
- Check IP Address via Router or Tool
- Log into your router’s admin panel (
192.168.1.1or similar). - Under Connected Devices, find your camera’s IP address and note it down for browser access.
- Log into your router’s admin panel (
🌐 C. Important Connection Tips
- Use the Same Network: Ensure your camera, NVR, and computer are all connected to the same router or switch.
- Avoid Wi-Fi Extenders: They can cause lag and disconnections.
- PoE Recommendation: If possible, choose PoE IP cameras — they’re cleaner, safer, and more reliable for professional setups.
- Distance Matters: Keep wireless cameras within 15–20 meters of the router for stable performance.
- Label Cables: If you’re connecting multiple cameras, label each Ethernet cable to avoid confusion later.
⚡ D. Quick Troubleshooting
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Camera not detected | Loose LAN cable or IP conflict | Reconnect and rescan with the IP tool |
| Wi-Fi setup failed | Wrong password or weak signal | Recheck password and move camera closer |
| No power light | Faulty adapter or PoE issue | Test adapter or switch port |
| No video in app | Camera not added properly | Re-add using QR or IP method |
Once your camera is powered on and successfully connected to the network, you’re ready for the next stage — finding your camera’s IP address and logging in through a web browser or software.
🔍 4. Step 2 – Finding the Camera’s IP Address
Once your IP CCTV camera is properly connected to the network — either via LAN cable (wired) or Wi-Fi — the next essential step is to find its IP address. This unique identifier allows you to access the camera’s settings, live feed, and recording options directly through a web browser or camera software.
Think of the IP address as your camera’s digital home address on your network. Without it, you cannot configure, monitor, or integrate it with an NVR (Network Video Recorder).
Let’s go step by step.
💡 What is an IP Address in CCTV Systems?
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique series of numbers (for example, 192.168.1.108) assigned to each device connected to a local network.
- Every IP CCTV camera you install receives its own unique IP.
- The NVR, router, and your computer also have their own IPs.
- To make them communicate properly, all devices must be in the same subnet range, e.g.,
192.168.1.x.
If your camera and computer are not in the same range, they won’t “see” each other on the network.
🧭 Step-by-Step Process to Find the IP Address
There are several easy ways to detect the camera’s IP address. The method depends on your camera brand and the setup type (wired or wireless).
🧰 Method 1: Using the Manufacturer’s IP Search Tool
Most professional CCTV brands (like Hikvision, Dahua, CP Plus, Uniview, Reolink, etc.) provide a free IP Finder utility that automatically scans your local network and lists all connected cameras.
🔧 Steps:
- Install the IP Search Tool from the camera’s official website or from the CD that came with your device.
- Open the software on your computer (make sure your PC is connected to the same router as the camera).
- Click “Search” or “Refresh.”
- The tool will display all available devices along with:
- IP address
- MAC address
- Device model
- Port number
- Firmware version
- Identify your camera using the model or MAC address printed on the camera’s body.
- Note down the IP address — for example,
192.168.1.108.
👉 Tip: If the IP address begins with something different like 192.0.0.x or 10.1.1.x, you may need to change it to match your local network (explained in the next step).

🌐 Method 2: Using Your Router’s Device List
If you can access your router’s admin page, you can easily locate the IP of your connected camera.
🧭 Steps:
- Open your browser and type your router’s login address (commonly
192.168.1.1or192.168.0.1). - Enter your router username and password.
- Go to the Connected Devices or DHCP Client List section.
- Look for your camera’s name (for example, “IPCAM”, “Hikvision”, “CP-PLUS-XXXX”).
- Note the IP address assigned to it by your router.
💡 Pro Tip: Rename your camera in the router’s device list to make it easier to recognize later.
🧩 Method 3: Using a Mobile App (For Wireless Cameras)
If you’re using a Wi-Fi camera connected via the manufacturer’s app, you can check the IP from within the app itself.
📱 Steps:
- Open the mobile app you used during setup (e.g., Imou Life, Hik-Connect, ezykam+).
- Go to the Device Settings or Network Information section.
- Look for the IP Address or Local Network Info tab.
- Note the IP address — you’ll use it to log in from your browser or NVR.
💻 Method 4: Using Command Prompt (For Advanced Users)
If you’re familiar with networking tools, you can use Command Prompt (Windows) to locate your camera’s IP.
⚙️ Steps:
- Open Command Prompt (
Win + R→ typecmd→ press Enter). - Type the command:
arp -a - Press Enter — this will list all active IP addresses on your network.
- Compare the list with your camera’s MAC address to find the correct one.
⚡ Common Issues & Fixes
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Camera not showing in IP search tool | Different network range or firewall blocking | Temporarily disable firewall and connect directly to router |
| Duplicate IP error | Another device using the same IP | Change one device’s IP manually |
| No device detected | LAN cable loose or PoE switch off | Reconnect and restart both camera and router |
| IP keeps changing | Router’s DHCP assigning new IP | Set a static IP address in the next configuration step |
🔑 Best Practice – Assigning a Static IP Address
To avoid future connection problems, assign a static IP to your camera (one that doesn’t change after every restart).
- Example: if your router’s range is
192.168.1.1to192.168.1.254, assign your camera something like192.168.1.120. - Subnet Mask:
255.255.255.0 - Gateway: Router’s IP (e.g.,
192.168.1.1)
A static IP ensures your NVR or mobile app always knows where to find the camera — even after reboots.
🧱 5. Step 3 – Accessing the Camera via Browser
Now that you’ve successfully found your IP CCTV camera’s IP address, the next major step is to access the camera interface using a web browser. This is where all the magic happens — you’ll log into the camera, adjust video settings, configure motion alerts, set recording parameters, and even fine-tune your network options.
Accessing the camera through a browser gives you complete administrative control over every aspect of your surveillance setup. Let’s explore this step in depth.
🌍 What Is the Camera Web Interface?
Every IP CCTV camera comes with an inbuilt web server that allows users to interact with it using a standard web browser like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, or Internet Explorer (for older models).
When you type the camera’s IP address (e.g., http://192.168.1.108) into the browser’s address bar, you’re directly connecting to that camera’s control panel. This interface displays live video and gives access to configuration settings like:
- Video quality and encoding
- Network setup (static IP, DDNS, etc.)
- Motion detection and alarm schedules
- User account management
- Firmware upgrades and maintenance
🧭 Step-by-Step Process to Access the Camera via Browser
Let’s break down the process clearly so you can log in smoothly without any errors.
🖥️ Step 1: Ensure the Camera and Computer Are on the Same Network
- Connect your PC or laptop to the same router as your camera (wired or Wi-Fi).
- Double-check that both are within the same IP range.
- Example:
- PC IP:
192.168.1.100 - Camera IP:
192.168.1.108
✅ Perfect — same subnet (192.168.1.x)
- PC IP:
- Example:
If they’re not in the same range, adjust the camera’s IP using the IP Configuration Tool you installed earlier.
🌐 Step 2: Open the Browser and Enter the IP Address
- Launch your preferred web browser.
- In the address bar, type your camera’s IP address, for example:
http://192.168.1.108 - Press Enter.
If everything is correctly connected, you’ll see the login page for your IP camera.
💡 Note: Some older cameras only support Internet Explorer due to ActiveX plugins. For those, use IE Mode in Microsoft Edge or download the brand’s official browser plugin.
🔐 Step 3: Log Into the Camera Interface
- On the login screen, enter the default username and password.
Common defaults include: BrandUsernamePasswordHikvisionadmin12345 or admin123DahuaadminadminCP PlusadminadminUniviewadmin123456Imou / Reolinkadmin(blank) or 123456 - If you’re logging in for the first time, you may be prompted to create a new strong password.
✅ Once logged in, you’ll land on the main dashboard, where you can view the live video feed and access configuration menus.
🎥 Step 4: Install Necessary Plugins (if prompted)
Some browsers may ask you to install a web video plugin to view live video directly.
- For example:
- Hikvision may request WebComponents or VSPlugin.
- Dahua might ask for SmartPSS Web Plugin.
- Download and install it as instructed.
- After installation, refresh the page or restart the browser.
⚠️ Tip: For modern cameras, many brands have shifted to HTML5-based web interfaces, which no longer require plugins — making them easier and more secure to use.
⚙️ Step 5: Explore the Camera Settings
Once inside, you’ll find various tabs or menus such as:
🎬 Live View
- Displays real-time footage from the camera.
- You can adjust stream quality (Main Stream / Sub Stream).
- Useful for verifying camera placement and focus.
🧰 Configuration / Setup
- Here you can adjust:
- Video resolution & frame rate
- Encoding type (H.264 / H.265)
- Brightness, contrast, and exposure
- Motion detection zones
- Recording schedules
🌐 Network Settings
- Change IP type to Static IP for stability.
- Configure Gateway, DNS, and Port Number (useful for remote access).
- Enable DDNS or P2P if supported.
👥 User Management
- Add or edit multiple users with different permission levels.
- Create a viewer-only account for general staff or clients.
📦 Storage
- Set up NVR recording, SD card storage, or NAS drive connection.
- Define overwrite options and recording time schedules.
🔔 Event & Alarm Setup
- Configure motion detection, tamper alarms, and email alerts.
- Adjust sensitivity to avoid false triggers.

🧠 Step 6: Save and Apply Settings
After making any changes, always click “Save” or “Apply” before leaving the page. Many users forget this, leading to lost configurations.
If prompted, the camera may reboot automatically to apply new settings. Wait for it to restart, then refresh your browser to continue.
🧰 6. Step 4 – Configuring Camera Network Settings
Once you’ve accessed your IP CCTV camera via a web browser, the next essential step is to properly configure the camera’s network settings. This stage determines how your camera communicates within your local network and connects to external devices such as NVRs, mobile apps, or cloud storage services.
Think of this step as setting up the camera’s “digital identity.” It ensures your camera stays connected, stable, and secure — even after power outages or network restarts.
🌍 Why Network Configuration Is Important
Without the right network settings, your camera might:
- Lose connection frequently
- Fail to appear on the NVR or mobile app
- Get assigned a new IP address each time the router restarts (DHCP issue)
- Be vulnerable to security threats
By setting a Static IP Address and optimizing ports, you ensure that your camera operates seamlessly 24/7.
⚙️ Step-by-Step Guide to Configure Network Settings
Let’s dive into the full process to set up your camera’s network the correct way.
🧩 Step 1: Access the Network Menu
- Log in to your camera’s web interface (via IP address in your browser).
- Navigate to the Configuration → Network → Basic Settings (menu names may vary slightly by brand).
- Here, you’ll see several tabs like:
- TCP/IP
- Port
- DDNS
- NTP (Time Sync)
- P2P or Cloud Access
🌐 Step 2: Change IP Type from DHCP to Static
By default, most cameras use DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), which means the router assigns a random IP each time. This can cause the NVR or app to lose the camera connection.
To fix this:
- Locate the “Obtain IP address automatically (DHCP)” checkbox.
- Uncheck it.
- Now, manually enter a Static IP address that’s within your router’s range but not currently in use.
Example Configuration:
- IP Address:
192.168.1.120 - Subnet Mask:
255.255.255.0 - Gateway:
192.168.1.1(usually your router’s IP) - Preferred DNS:
8.8.8.8(Google DNS) - Alternate DNS:
8.8.4.4(Backup DNS)
Click Save / Apply to store the new settings.
💡 Pro Tip: Keep a note of the assigned IP address — you’ll use it later when adding cameras to your NVR or mobile app.
🧠 Step 3: Configure Port Settings
Ports are like digital doorways through which your camera sends and receives data. Setting them correctly is vital, especially if you want to access your camera remotely.
You’ll typically find a Port Configuration section under Network Settings → Port.
Common ports include:
| Type | Purpose | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| HTTP | Accessing via browser | 80 |
| RTSP | Live video streaming | 554 |
| Server / Media | Communication with NVR | 8000 |
| HTTPS | Secure encrypted access | 443 |
If your network uses multiple cameras, change the ports slightly for each one to avoid conflicts. For example:
- Camera 1 → HTTP 81, RTSP 554
- Camera 2 → HTTP 82, RTSP 555
Click Save after making any changes.
📡 Step 4: Enable DDNS (Dynamic DNS) – Optional for Remote Access
If you plan to view your camera remotely (outside your local network), you’ll need a DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name System) setup.
This feature links your camera to a domain name (like myshopcam.ddns.net) that updates automatically whenever your public IP changes.
To enable DDNS:
- Go to Network → DDNS Settings.
- Choose a DDNS provider like No-IP, DynDNS, or your camera brand’s built-in service.
- Enter your credentials and host name.
- Enable DDNS and click Save.
Now you can access your camera from anywhere using your chosen DDNS address instead of typing your dynamic IP manually.
⏰ Step 5: Sync Camera Time (NTP Configuration) Configure IP CCTV Camera
Correct time synchronization is essential for accurate video logs and event tracking.
To set it up:
- Navigate to Network → NTP Settings.
- Enable NTP (Network Time Protocol).
- Enter a reliable server like:
pool.ntp.orgortime.google.com
- Set your Time Zone (e.g., +05:30 for India).
- Click Sync Now and then Save.
This ensures that all your recordings, motion alerts, and logs have the correct timestamps.
☁️ Step 6: Enable P2P or Cloud Access (Optional but Recommended) Configure IP CCTV Camera
Modern IP CCTV cameras often support P2P (Peer-to-Peer) connections — a cloud-based feature that allows remote viewing via a smartphone app without needing manual port forwarding.
To enable it:
- Go to Network → P2P or Cloud Settings.
- Toggle Enable P2P.
- Wait for the Status to change to “Online.”
- Open the camera’s mobile app (e.g., Hik-Connect, Imou Life, ezykam+) and scan the QR code displayed on the screen.
Once added, you can now view your camera remotely on your phone anytime, anywhere. Configure IP CCTV Camera
🔒 Security Recommendations
- Change Default Passwords Immediately: Use a strong password with letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Disable Unused Services: Turn off FTP, SNMP, or Telnet if you’re not using them.
- Restrict Network Access: Allow only trusted devices or static IPs to access the camera.
- Keep Firmware Updated: Always update to the latest version to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Backup Configuration: After finalizing settings, export and save your configuration file. Configure IP CCTV Camera
⚡ Common Issues & Solutions
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Camera disconnects frequently | Using DHCP instead of static IP | Set static IP manually |
| NVR can’t detect camera | Port mismatch or IP conflict | Recheck port numbers and IP range |
| Time on footage incorrect | NTP not configured | Enable and sync NTP |
| Remote access fails | Router not forwarding ports / DDNS misconfigured | Enable P2P or correct DDNS settings |
🧱 In Summary
Configuring your camera’s network settings is the foundation of a stable, secure CCTV system. A properly configured network ensures smooth live streaming, consistent recording, and reliable remote monitoring.
After this step, your camera becomes fully integrated into your network — ready to record, alert, and protect.
You’re now ready for the next crucial phase:
🎥 Step 5 – Setting Up Recording, Motion Detection & Alerts. Configure IP CCTV Camera

🎥 7. Step 5 – Adding Camera to NVR or Software
If you are using an NVR (Network Video Recorder):
- Login to your NVR interface (locally or via web).
- Go to Camera Management / Add Camera.
- Click Add Manually and enter:
- Camera IP Address
- Username & Password
- RTSP Port (usually 554)
- Once connected, you’ll see live video on your NVR screen. Configure IP CCTV Camera
If using PC software (like iVMS, SmartPSS, or CP Plus NVMS), repeat the same process from the software’s Device Management section.
📱 8. Step 6 – Enabling Remote Viewing (Mobile Access)
To monitor your CCTV from anywhere in the world:
- Install the manufacturer’s mobile app:
- Hik-Connect (Hikvision)
- iDMSS or gDMSS (Dahua)
- ezykam+ (CP Plus)
- Register your account on the app.
- Scan the QR code on the camera or NVR.
- Add device → Save → You can now view live feed remotely!
Make sure your camera or NVR is connected to the internet and P2P (Peer-to-Peer) option is enabled in settings. Configure IP CCTV Camera
🔔 9. Step 7 – Configuring Motion Detection & Alerts
Most IP cameras come with smart motion detection features.
You can configure them as follows:
- Go to Event / Motion Detection in the camera interface.
- Enable the feature and select detection area.
- Set Sensitivity Level (medium recommended).
- Configure Email or Mobile Alerts.
- Save settings and test motion-triggered notifications.
🔄 10. Step 8 – Firmware Update & Security Settings
Always keep your IP CCTV camera up-to-date to prevent hacking and bugs:
- Visit the manufacturer’s website for the latest firmware version.
- Update through the Device Maintenance or Upgrade menu.
- Change default ports (HTTP, RTSP) for added protection.
- Use a strong password with letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Disable remote access if not required.
🧩 11. Step 9 – Storage Configuration (Local & Cloud)
You can store recordings in multiple ways:
- MicroSD Card: Insert directly into the camera for local storage.
- NVR Storage: Use HDD inside NVR for 24×7 recording.
- Cloud Storage: Some IP cameras support paid cloud plans for remote backup.
In the Recording Settings menu, select:
- Continuous Recording
- Motion-Based Recording
- Schedule Recording (specific hours) Configure IP CCTV Camera
⚙️ 12. Step 10 – Testing and Final Verification
Once all configurations are done:
- Test live view on both local and remote devices.
- Check playback and backup features.
- Ensure all cameras have stable connectivity.
- Verify notifications and motion alerts.
A quick stability check for 24 hours ensures your system runs flawlessly.
🧠 13. Troubleshooting Common IP Camera Issues
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Camera not showing in network | IP conflict or wrong cable | Assign new IP or replace cable |
| Cannot access via browser | Plugin or browser issue | Use IE/Edge or install ActiveX |
| No image in app | Port or P2P disabled | Enable P2P or port forwarding |
| Motion alerts not working | Feature disabled | Enable detection zone and sensitivity |
| No recording | Storage not formatted | Format SD card or HDD properly |
🔐 14. Expert Tips for Optimized IP Camera Performance
Configuring your IP CCTV system correctly is only half the battle — keeping it performing at its maximum efficiency is where true expertise comes in. Whether you’re securing a business, office, or home, even a perfectly installed IP camera can underperform if not optimized for speed, clarity, and reliability.
Below are expert-level tips that help ensure your IP CCTV cameras operate smoothly, record efficiently, and remain stable for years to come.
⚙️ 1. Use High-Quality Network Equipment
Your camera’s performance heavily depends on your network quality.
- Always use Cat6 Ethernet cables for long-distance connections (up to 100 meters).
- Invest in a Gigabit PoE switch — it ensures smooth power and data transmission without lag.
- For Wi-Fi cameras, use dual-band routers (2.4GHz + 5GHz) to reduce interference.
🧠 Pro Tip: Avoid cheap network cables — they often degrade signal quality and lead to frame drops in HD video streams.
💾 2. Choose the Right Storage Solution
Recording high-resolution video 24/7 requires robust storage management.
- Use Surveillance-grade Hard Drives (e.g., WD Purple, Seagate SkyHawk). These are designed for continuous writing operations.
- Regularly check storage health in the NVR settings.
- Set a loop recording mode so older footage automatically overwrites when space is full.
🧠 Pro Tip: Calculate required storage using bitrate × hours × number of cameras. This ensures you don’t run out of space unexpectedly.
📶 3. Assign Static IPs to All Cameras
Never rely on DHCP for CCTV cameras. A static IP prevents disconnections when the router reboots.
- Keep IPs in a consistent format (e.g.,
192.168.1.101,192.168.1.102, etc.). - Maintain a document listing each camera’s IP, name, and location for quick troubleshooting.
🧠 Pro Tip: Reserve IP addresses in the router to avoid IP conflicts when adding new devices.
🎥 4. Optimize Video Quality and Bitrate
High resolution isn’t always the best choice. Balance video quality with available bandwidth.
- Use H.265 or H.265+ compression for efficient storage without sacrificing clarity.
- For outdoor areas, use 1080p or 2K resolution. For indoor spaces, 720p may suffice.
- Adjust the bitrate between 2048–4096 Kbps depending on your network speed.
🧠 Pro Tip: Set your camera to Variable Bitrate (VBR) — it automatically adjusts compression for motion-heavy scenes.
🌙 5. Enhance Night Vision Performance
Low-light recording can make or break your security coverage.
- Ensure IR LEDs are clean and not covered by dirt or cobwebs.
- Avoid placing cameras behind glass; it causes IR reflection and white glare.
- Use cameras with Smart IR or Starlight Technology for better night performance.
🧠 Pro Tip: Add a small external IR illuminator for large or dark outdoor areas.
🔔 6. Fine-Tune Motion Detection and Alerts
Smart motion detection helps save storage and minimize false alarms.
- Adjust motion sensitivity so minor movements (like shadows or insects) don’t trigger alerts.
- Define custom motion zones — only monitor critical areas like doors or driveways.
- Enable email or push notifications for instant alerts.
🧠 Pro Tip: Schedule motion detection to activate only during off-hours for business premises.
🔋 7. Keep Firmware and Software Updated
Camera manufacturers frequently release updates to improve performance and security.
- Check for firmware updates every 2–3 months.
- Update both the camera and NVR firmware.
- Always backup configuration files before upgrading.
🧠 Pro Tip: Enable “auto-update notifications” in your camera settings to stay informed.
🧱 8. Secure Your Network and Cameras
Security is just as important as video quality. Protect your CCTV system from hacking attempts.
- Change default passwords immediately after setup.
- Use HTTPS and strong encryption where possible.
- Disable unused services like FTP, SNMP, or Telnet.
- Keep cameras behind a firewall or VLAN.
🧠 Pro Tip: Enable two-factor authentication if your camera’s mobile app supports it.
💡 9. Adjust Camera Placement Strategically
Proper placement ensures you capture useful footage with minimal blind spots.
- Mount cameras at a height of 9–12 feet for the best view angle.
- Avoid direct sunlight or strong lights shining into the lens.
- Ensure the camera covers key areas — entry points, gates, and cash counters.
🧠 Pro Tip: Use a wide-angle lens for small rooms and a zoom lens for long corridors.
🌐 10. Monitor Bandwidth Usage
Streaming multiple IP cameras can strain your network.
- Check your router’s dashboard or NVR bandwidth report.
- Use lower bitrates on non-critical cameras to save bandwidth.
- Avoid watching all camera feeds in HD simultaneously unless required.
🏁 Conclusion – Smarter Security Starts with Proper Configuration
Setting up an IP CCTV camera might seem technical, but with the right approach, it’s straightforward and rewarding. Once properly configured, your cameras will provide 24×7 peace of mind, whether you’re monitoring your home, office, or business.
Remember — security is not just about buying a camera; it’s about configuring it smartly, maintaining it regularly, and staying connected.
If you’re based in Durgapur, you can reach out to Mithu Tech or Gitakart Digital Pvt. Ltd. for professional installation and configuration services. Both are recognized leaders in CCTV and networking solutions, ensuring reliable setup and after-sales support.
Discover more from Mithu Tech Group
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
