Blog
How to Configure CCTV NVR, Step-by-Step Setup for Beginners & Professionals
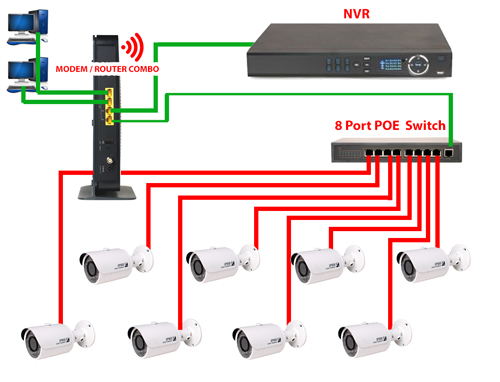
How to Configure CCTV NVR: In today’s surveillance-driven world, NVR (Network Video Recorder) systems are becoming the cornerstone of modern security setups. Unlike traditional DVRs, NVRs offer network-based recording, better resolution, and seamless integration with IP cameras. Whether you are setting up a home security system or a commercial CCTV network, understanding how to configure your NVR correctly is essential for reliable video monitoring.
This guide will walk you through every step of NVR configuration, from hardware setup to remote access, ensuring your security system is fully functional and optimized.
1. Understanding NVR – What is a Network Video Recorder?
A Network Video Recorder (NVR) is a digital device designed to record, store, and manage video footage from IP cameras over a network. Unlike traditional DVRs (Digital Video Recorders) that work with analog cameras and coaxial cables, NVRs rely on network connectivity to capture high-definition video streams from IP-based surveillance cameras.
Key Features of an NVR:
- IP Camera Integration – Supports multiple cameras over Ethernet or PoE.
- High-Resolution Recording – Handles Full HD and 4K video quality.
- Remote Access – Monitor footage in real-time via smartphones, tablets, or computers.
- Motion Detection & Alerts – Triggers recording or notifications when movement is detected.
- Scalable Architecture – Easily add more cameras without major rewiring.

NVR vs DVR – Why NVR is Preferred Today
| Feature | NVR | DVR |
|---|---|---|
| Camera Type | IP cameras | Analog cameras |
| Video Quality | HD / 4K | Standard Definition |
| Network | Ethernet / Wi-Fi | Coaxial Cable |
| Remote Access | Yes, via app or web | Limited |
| Installation | Easier with PoE | More complex wiring |
In short, an NVR simplifies surveillance while providing high-quality video, flexible installation, and smarter management options, making it ideal for home, office, and commercial security systems.
2. Pre-Setup Requirements
Before you start configuring your NVR (Network Video Recorder), it’s essential to gather all the necessary components and plan your setup. Proper preparation ensures a smooth installation, prevents technical issues, and optimizes system performance for CCTV surveillance.
Essential Hardware and Tools
- NVR Device
- Choose an NVR compatible with your IP cameras and supporting the number of channels you need (4, 8, 16, or more).
- Check for PoE support if you want simplified cabling.
- IP Cameras
- Ensure cameras are compatible with your NVR (ONVIF standard recommended).
- Decide between dome, bullet, or PTZ cameras based on your monitoring requirements.
- PoE cameras simplify installation, while non-PoE cameras may require separate power adapters.
- Monitor/TV
- Connect your NVR to a monitor via HDMI or VGA to view live feeds and navigate the interface.
- Mouse and Keyboard
- Needed for navigating the NVR menu and performing configurations.
- Network Equipment
- Router or switch for connecting IP cameras to the network.
- Ethernet cables (Cat5e or Cat6 recommended) for reliable wired connections.
- Storage Drives
- Install HDD or SSD compatible with your NVR for video storage.
- Surveillance-grade hard drives are recommended for continuous recording.
Software and App Requirements
- Mobile or desktop apps provided by the NVR manufacturer for remote access.
- Optional firmware updates to ensure your NVR runs the latest security and performance enhancements.
Environmental Considerations
- Choose a secure and ventilated location for the NVR to prevent overheating.
- Ensure cameras have a clear field of view and proper lighting conditions.
- Avoid locations with excessive moisture or dust that may damage the equipment.
Checklist Before You Begin
| Task | Status |
|---|---|
| Verify NVR and camera compatibility | ✅ |
| Check power supply availability | ✅ |
| Ensure stable network connection | ✅ |
| Prepare Ethernet cables and connectors | ✅ |
| Install storage drive (HDD/SSD) | ✅ |
| Update NVR firmware | ✅ |
Proper preparation at this stage saves hours of troubleshooting later and ensures your NVR system operates efficiently from day one.
3. Physical Installation of NVR
Once you’ve completed the pre-setup requirements, the next step is the physical installation of your NVR (Network Video Recorder). Proper installation ensures optimal camera performance, network connectivity, and long-term reliability for your CCTV security system.
Step 1: Choose the NVR Location
- Select a secure, dry, and ventilated area to prevent overheating.
- Ensure the location is near a network router or switch if using wired IP cameras.
- Avoid direct sunlight, high humidity, or dust-prone areas that could damage the device.
- If the NVR will be installed in a rack, ensure adequate airflow around the unit.
Step 2: Connect IP Cameras to the NVR
Option A: Using PoE (Power over Ethernet) NVR
- Plug each IP camera into the NVR’s PoE ports using Cat5e or Cat6 cables.
- PoE eliminates the need for separate power adapters, simplifying the installation process.
Option B: Using Non-PoE Cameras
- Connect cameras to a network switch or router using Ethernet cables.
- Supply power separately using adapters or a centralized power source.
- Make sure cameras and NVR are on the same local network for detection.
Step 3: Connect Monitor and Mouse
- Use an HDMI or VGA cable to connect your NVR to a monitor or TV.
- Plug in a USB mouse for navigating the NVR menu and performing configuration.
- Some NVRs may also support remote configuration via mobile or web apps, but initial setup is easier with a monitor and mouse.
Step 4: Install Storage (HDD/SSD)
- Open the NVR’s storage bay and install a compatible hard disk drive (HDD) or SSD.
- Secure the drive properly and format it via the NVR menu to enable recording.
- Surveillance-grade HDDs are recommended for continuous video recording.
Step 5: Power Up the NVR and Cameras
- Connect the NVR to a stable power source using the provided adapter.
- Power on all cameras and ensure they initialize properly.
- Wait for the NVR to boot up completely, usually indicated by LED lights or a startup screen.
Step 6: Check Connectivity
- Verify that all cameras are visible on the monitor’s live view screen.
- If any camera feed is missing, check the cabling, IP addresses, and network connection.
- Ensure PoE cameras are receiving power if connected through PoE ports.
Step 7: Organize Cables and Secure Equipment
- Use cable ties or conduits to manage Ethernet and power cables neatly.
- Avoid loose or tangled wires that could cause connection issues or damage.
- Label each camera and its corresponding NVR channel for easier management.
Pro Tip: Always keep your NVR firmware updated before adding cameras. This ensures better compatibility and security for your CCTV system.
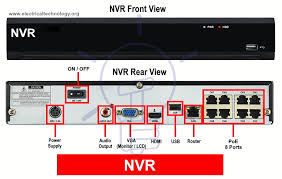
4. Initial NVR Configuration
After physically installing your NVR (Network Video Recorder) and connecting all cameras, the next crucial step is the initial software configuration. Proper configuration ensures your CCTV system records reliably, streams smoothly, and can be accessed remotely.
Step 1: Power On and Access NVR Interface
- Turn on the NVR and ensure all connected cameras are receiving power.
- Connect a monitor via HDMI or VGA to view the NVR’s interface.
- Use the USB mouse to navigate through menus.
- Wait for the system to boot fully; this usually takes a few minutes.
Step 2: Language, Date, and Time Settings
- Select your preferred language for the NVR menu.
- Set the correct date, time, and time zone to ensure accurate timestamping of recorded footage.
- Enable automatic daylight saving adjustments if supported.
- Correct time settings are critical for playback, alerts, and remote access.
Step 3: Admin Account and Password Setup
- Change the default username and password for the administrator account.
- Create a strong password combining letters, numbers, and symbols to secure your NVR from unauthorized access.
- Some NVRs allow creating additional user accounts with limited access for other staff or family members.
Step 4: Network Configuration
- Navigate to Network Settings in the NVR menu.
- Choose either DHCP (automatic IP assignment) or Static IP (manual IP configuration).
- DHCP: NVR receives an IP automatically from the router.
- Static IP: Assign a fixed IP to ensure stable remote access.
- Set subnet mask, gateway, and DNS servers if using a static IP.
- Test network connectivity using the Ping test (most NVRs provide this option).
Step 5: Date, Time Synchronization via NTP (Optional)
- Enable NTP (Network Time Protocol) to sync the NVR clock automatically with internet time servers.
- This ensures all footage is timestamped accurately, especially important for legal or business surveillance.
Step 6: Enable Remote Access
- Most modern NVRs support P2P cloud access.
- Enable P2P and scan the QR code using the mobile app provided by the manufacturer.
- For manual setup, configure port forwarding on your router for remote access via web browser or app.
Step 7: Firmware Updates
- Check for latest firmware updates for both the NVR and connected IP cameras.
- Firmware updates fix bugs, improve stability, and enhance security features.
- Apply updates before proceeding with advanced configuration.
Step 8: Initial Camera Check
- Ensure all connected cameras display live video feed on their respective channels.
- Adjust camera names, channels, and ordering in the NVR menu.
- Test PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) functions, if applicable, to verify camera control.
5. Adding IP Cameras to Your NVR
Once your NVR (Network Video Recorder) is installed and initially configured, the next critical step is adding IP cameras. Properly adding cameras ensures that all areas of your property are monitored, and your system records footage reliably. Most modern NVRs support both automatic and manual camera addition, making setup easy for beginners and advanced users alike.
Step 1: Automatic Camera Detection
Most NVRs come with a plug-and-play feature that automatically detects connected IP cameras on the same network.
- Navigate to Camera Management → Add Camera → Search in your NVR menu.
- The NVR will scan the network and display a list of all available IP cameras.
- Select the cameras you want to add and assign them to specific channels (Channel 1, 2, 3, etc.).
- Verify the live video feed for each camera to ensure proper connectivity.
Pro Tip: Make sure your cameras are powered and connected via Ethernet or PoE before performing the automatic search.
Step 2: Manual Camera Addition
Manual addition is useful when your NVR doesn’t detect a camera automatically or when adding cameras from a different network segment.
- Go to Camera Management → Add Camera → Manual Add.
- Enter the camera’s IP address, username, and password.
- Assign the camera to the desired channel number.
- Click Apply and check the live feed to ensure the connection works.
Tip: Always check that the camera’s IP address is in the same subnet as your NVR to avoid connectivity issues.
Step 3: Camera Naming and Organization
- Assign descriptive names to each camera (e.g., “Front Gate,” “Lobby,” “Warehouse”).
- Proper naming helps during playback, alerts, and remote monitoring.
- Organize channels logically, prioritizing high-risk areas first.
Step 4: Testing Camera Feed
- After adding all cameras, navigate through each channel to verify live video streaming.
- Check image clarity, angles, and lighting conditions.
- Adjust camera positioning if necessary for full coverage.
Step 5: Troubleshooting Camera Connectivity
| Issue | Possible Solution |
|---|---|
| Camera not detected | Check cables, power, and network connection |
| No live feed | Verify IP address, username/password, and network settings |
| Feed lagging | Check network bandwidth and adjust resolution/frame rate |
| PoE camera not powering | Ensure PoE port is active and supports required wattage |
Step 6: Group Cameras (Optional Advanced Feature)
- Some NVRs allow grouping cameras by area, floor, or function.
- This feature is helpful for large systems, making monitoring and playback more organized.
- Enable group alerts to receive notifications from multiple cameras simultaneously.

6. Configuring Recording Settings
After successfully adding IP cameras to your NVR (Network Video Recorder), the next crucial step is configuring recording settings. Proper recording configuration ensures that your CCTV system captures critical events efficiently, saves storage space, and allows for easy playback.
Step 1: Choose the Recording Mode
Most NVRs offer multiple recording modes to suit different surveillance needs:
- Continuous Recording
- The camera records 24/7, capturing everything.
- Ideal for high-security areas but consumes more storage.
- Scheduled Recording
- Record only during specific times of the day (e.g., office hours).
- Helps conserve storage while still monitoring critical periods.
- Motion Detection Recording
- Records only when movement is detected within predefined zones.
- Reduces storage usage and makes reviewing footage faster.
- Event-Triggered Recording
- Records based on alarms, door sensors, or other integrated devices.
- Perfect for automated security systems.
Step 2: Set Resolution and Frame Rate
- Resolution: Choose between 720p, 1080p, or 4K depending on camera capabilities and storage availability.
- Frame Rate: A higher frame rate (e.g., 30 fps) provides smoother video but uses more storage; a lower frame rate saves storage.
- Balance quality and storage based on your needs.
Pro Tip: For critical areas like entrances or cash registers, prioritize higher resolution and frame rate.
Step 3: Configure Storage Settings
- Install and Format HDD/SSD
- Ensure your storage drive is installed and formatted correctly in the NVR.
- Set Recording Overwrite
- Enable automatic overwrite to replace the oldest footage once storage is full.
- This ensures continuous recording without interruptions.
- Storage Management Tips:
- Use surveillance-grade HDDs for durability.
- Consider multiple drives for high-capacity setups.
- Monitor disk health periodically.
Step 4: Configure Recording Schedule
- Navigate to Recording Schedule in the NVR menu.
- Assign recording modes for each camera per time slot.
- Example: Motion detection for nighttime, continuous during office hours.
- Use color-coded schedules if your NVR supports it for easy visualization.
Step 5: Motion Detection & Recording Zones
- Enable motion detection for cameras where needed.
- Define zones within the camera’s field of view to focus on important areas.
- Adjust sensitivity to avoid false alarms caused by small movements like pets or trees.
Step 6: Test Your Recording Setup
- After configuring, test by triggering motion in different zones.
- Check that the NVR captures events correctly and stores them on the HDD.
- Review playback speed, clarity, and timestamp accuracy to ensure proper setup.
Pro Tip: Regularly check recording logs and storage status to prevent missed footage. Combining motion detection with scheduled recording is a best practice for balancing security and storage efficiency.
7. Configuring Motion Detection & Alerts
One of the most powerful features of modern NVR (Network Video Recorder) systems is motion detection and alert notifications. Proper configuration ensures that you are instantly informed of any suspicious activity, helping prevent security breaches and improving overall monitoring efficiency.
Step 1: Enable Motion Detection for Cameras
- Navigate to Camera Settings → Motion Detection in your NVR menu.
- Select the camera(s) for which you want to enable motion detection.
- Toggle Motion Detection ON.
- Adjust the detection area by selecting zones within the camera’s field of view.
- Focus on entrances, hallways, or restricted areas.
- Exclude irrelevant areas like roads or trees that may cause false alerts.
Step 2: Adjust Sensitivity and Threshold
- Sensitivity: Determines how easily the camera detects movement.
- High sensitivity = detects small movements (may trigger false alarms).
- Low sensitivity = detects larger movements only.
- Threshold: Sets the minimum size or intensity of movement that triggers recording or alerts.
Tip: Test different sensitivity settings to balance detection accuracy with false alarm prevention.
Step 3: Configure Alerts and Notifications
- Email Alerts:
- Enter a valid email address in the NVR settings.
- Enable notifications for motion events, recording failures, or camera disconnections.
- Some Network Video Recorder allow attaching snapshots from the camera in alert emails.
- Push Notifications (Mobile App):
- Install the official Network Video Recorder mobile app.
- Log in and enable motion-triggered push notifications.
- Ensure your phone has internet connectivity for real-time alerts.
- Alarm Outputs (Optional):
- Some Network Video Recorder support external alarm devices like sirens or lights that activate upon motion detection.
- Configure alarm duration and triggers for additional security.
Step 4: Schedule Motion Detection
- Motion detection can be active 24/7 or during specific hours.
- Example: Activate motion alerts after office hours or when no one is home.
- Use the Network Video Recorder schedule settings to automate activation, saving storage and reducing unnecessary alerts.
Step 5: Test Motion Detection and Alerts
- Walk through the camera’s detection zone to simulate motion.
- Verify that:
- The Network Video Recorder starts recording as configured.
- Alerts are sent via email or app notifications.
- Any connected alarms are triggered (if applicable).
- Adjust sensitivity or zones if alerts are too frequent or missed.

8. Remote Access & Mobile App Configuration
One of the biggest advantages of a modern NVR (Network Video Recorder) system is the ability to access live feeds and recorded footage remotely. With proper setup, you can monitor your CCTV system from anywhere in the world using a smartphone, tablet, or computer. This ensures peace of mind and enhances security for both homes and businesses.
Step 1: Enable Remote Access on Your NVR
- Go to the NVR menu and navigate to Network → P2P / Cloud / Remote Access.
- Enable P2P (Peer-to-Peer) connection or the equivalent cloud-based service provided by your NVR brand.
- Take note of the device ID or QR code displayed on the NVR.
- Ensure your NVR is connected to the internet via Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
Pro Tip: P2P is easier for beginners because it eliminates complex router configurations like port forwarding.
Step 2: Configure DDNS (Optional for Manual Setup)
If your NVR does not support P2P or you prefer a static setup:
- Navigate to Network → DDNS.
- Register a DDNS account with the service your Network Video Recorder supports.
- Enter your hostname, username, and password in the Network Video Recorder.
- This allows you to access the Network Video Recorder using a fixed domain name instead of a changing IP address.
Note: Ensure your router supports port forwarding for HTTP and RTSP ports to enable remote viewing.
Step 3: Download and Install the Mobile App
- Search for your Network Video Recorder brand’s official mobile app (e.g., SmartPSS, Network Video Recorder Pro, or proprietary apps).
- Install the app on your iOS or Android device.
- Open the app and select Add Device → Scan QR Code or Enter Device ID.
- Log in using your Network Video Recorder admin username and password.
Step 4: Test Live Video Streaming
- Once connected, check all camera feeds to ensure live video is streaming smoothly.
- Adjust resolution and bandwidth settings in the app for optimal performance.
- Test both Wi-Fi and mobile data connectivity to ensure remote access works under different networks.
Step 5: Configure Mobile Notifications
- Enable motion alerts, recording notifications, and alarm triggers within the app.
- Choose how you want to receive notifications: push notifications, email alerts, or both.
- Test notifications by triggering motion in front of a camera.
Step 6: Remote Playback
- Most mobile apps allow playback of recorded footage stored on the Network Video Recorder.
- Select the camera, date, and time to review events.
- Use features like fast-forward, pause, snapshot, and download clips for evidence.
Step 7: Security Best Practices for Remote Access
- Always use a strong password and change default credentials.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) if the app supports it.
- Regularly update the app and Network Video Recorder firmware to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Avoid connecting to public Wi-Fi networks without VPN protection when accessing the Network Video Recorder.
9. Firmware Updates & Security Best Practices
Maintaining your NVR (Network Video Recorder) system goes beyond installation and configuration. Regular firmware updates and following security best practices are essential for ensuring stable performance, preventing unauthorized access, and protecting your CCTV system from cyber threats.
Step 1: Check for Firmware Updates
- Access your NVR menu and navigate to System → Firmware Upgrade or Maintenance → Update.
- Check the current firmware version installed on your NVR and cameras.
- Visit the manufacturer’s official website to download the latest firmware if it’s not available directly on the Network Video Recorder.
- Apply the update according to the instructions—most NVRs allow updating via USB drive or network download.
Pro Tip: Always backup your Network Video Recorder settings before performing a firmware update to avoid losing configurations.
Step 2: Benefits of Firmware Updates
- Enhanced Security: Protects against known vulnerabilities and hacking attempts.
- Bug Fixes: Resolves glitches and improves stability.
- New Features: Access improved functions, better remote access, and optimized performance.
- Compatibility: Ensures your Network Video Recorder works seamlessly with newer IP cameras.
Step 3: Strong Password Policies
- Avoid using default usernames and passwords for Network Video Recorder and cameras.
- Create strong passwords combining letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Change passwords periodically and after any personnel changes.
Step 4: Network Security Best Practices
- Use a secure network: Ensure your NVR is connected to a private, encrypted network.
- Enable firewalls: Protect your system from unauthorized external access.
- Port management: Only open necessary ports for remote access and avoid exposing unnecessary ports.
- VPN Access: For advanced security, access your NVR remotely via a VPN.
Step 5: Regular System Checks
- Periodically review recording schedules, motion detection logs, and storage usage.
- Check for camera connectivity issues or missing footage.
- Verify that remote access is functioning correctly and that alerts are being delivered.
Step 6: Backup & Data Management
- Regularly backup critical footage to an external hard drive or cloud storage.
- Enable automatic overwrite to prevent storage from filling up and missing important events.
- Maintain an organized folder structure for easy retrieval of recorded footage.
Step 7: Protect Against Physical Tampering
- Install Network Video Recorder in secure locations accessible only to authorized personnel.
- Use lockable racks or cabinets to prevent unauthorized physical access.

10. Troubleshooting Common NVR Issues
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Cameras not detected | Check network cables, IP conflicts, camera power |
| No live feed | Ensure correct IP, username, password; check network |
| Remote access fails | Verify router settings, DDNS, and port forwarding |
| Network Video Recorder keeps rebooting | Update firmware, check power supply, inspect HDD |
11. Tips for Optimized NVR Performance
After setting up and configuring your NVR (Network Video Recorder), it’s essential to adopt practices that maximize performance, reliability, and longevity. Optimized Network Video Recorder performance ensures your CCTV system operates smoothly, footage is recorded without interruptions, and remote access is seamless.
1. Use PoE Cameras When Possible
- PoE (Power over Ethernet) cameras receive both power and data through a single Ethernet cable.
- Reduces cabling complexity and installation cost.
- Ensures stable power supply, preventing camera downtime.
2. Choose High-Capacity, Surveillance-Grade Storage
- Install surveillance-grade HDDs or SSDs designed for 24/7 recording.
- High-capacity drives reduce the need for frequent overwriting.
- Regularly monitor storage health and free space to avoid recording interruptions.
3. Organize Cameras Logically
- Assign channels and camera names clearly (e.g., “Front Door,” “Lobby,” “Parking Lot”).
- Prioritize high-risk areas for first channels to streamline monitoring.
- Use grouping features if your Network Video Recorder supports zones or areas.
4. Schedule Regular Maintenance
- Clean camera lenses to maintain clear video quality.
- Inspect cables, connectors, and power sources periodically.
- Reboot the Network Video Recorder occasionally to ensure stable operation.
- Check for firmware updates for both NVR and cameras.
5. Optimize Recording Settings
- Balance resolution and frame rate for each camera according to importance.
- Use motion detection for low-risk areas to save storage.
- Regularly verify recording schedules and adjust based on changing security needs.
6. Enable Alerts and Notifications
- Set up motion detection alerts for critical areas.
- Ensure email or push notifications are functioning for real-time monitoring.
- Test alerts periodically to confirm the system is actively monitoring.
7. Secure Your NVR Network
- Use strong passwords and change them periodically.
- Restrict remote access to trusted devices.
- Consider a VPN for enhanced security when accessing the Network Video Recorder remotely.
8. Backup Critical Footage
- Regularly backup important footage to an external HDD or cloud storage.
- Maintain a systematic archive for easy retrieval in case of incidents.
9. Monitor System Performance
- Keep an eye on CPU usage, network bandwidth, and storage consumption.
- Address slow playback or lag immediately to prevent missed recordings.
- Adjust camera resolution or frame rate if network congestion occurs.
Pro Tip: Following these optimization tips ensures that your Network Video Recorder system remains reliable, efficient, and secure, providing consistent surveillance coverage for your property or business.
12. Conclusion – How to Configure CCTV NVR
Configuring an Network Video Recorder for CCTV is a critical step in securing your home, office, or business premises. By following this step-by-step guide, you can ensure reliable recording, remote monitoring, and efficient storage management. Whether you are a beginner or a professional installer, mastering Network Video Recorder setup ensures peace of mind and maximum security for your property.
Discover more from Mithu Tech Group
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.



